nOps Kubernetes Agent Overview
The nOps Kubernetes Agent stack is a helm chart that contains agent components that both gather metrics data in your Kubernetes cluster and enable nOps automated optimization of Karpenter and Container Rightsizing.
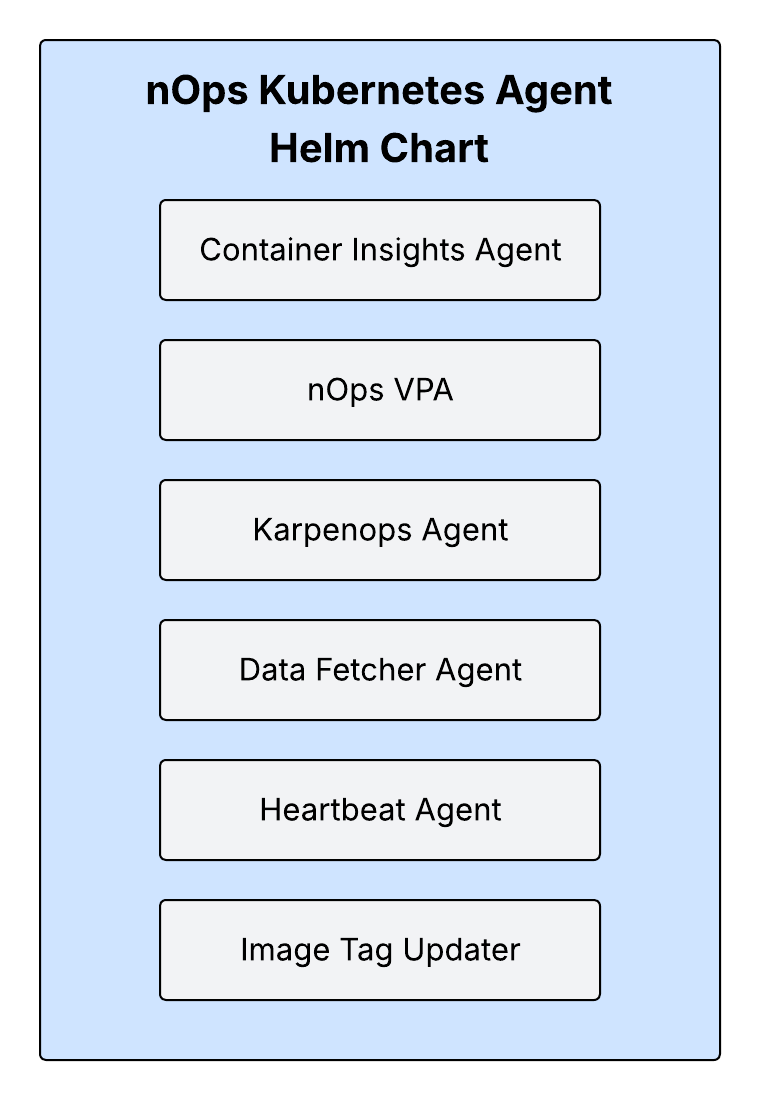
Agent Stack Components
- Container Insights Agent: The Container Insights agent is responsible for gathering all of the metrics nOps needs within your cluster.
- nOps VPA: The nOps Vertical Pod Autoscaler (VPA) is an agent that enables automated container rightsizing within your cluster
- Karpenops Agent: The Karpenops Agent is an agent that enables nOps to automatically optimize the Karpenter configuration of your cluster.
- Data Fetcher Agent: The Data Fetcher Agent gathers real-time information about the workloads in your cluster to enable the Workloads tab on your cluster dashboard in the nOps application
- Heartbeat Agent: The Hearbeat Agent syncs the status of the components in the agent stack with the nOps API to warn of any connectiveity issues
- Image Tag Updater: The Image Tag Updater automatically updates the image versions of the containers in the agent stack, so you can stay up to date without re-running any Helm commands
All of the agent stack components are managed, deployed, and updated by the Kubernetes Agent Helm chart. All components are installed into the nops namespace by default.
Deployment Workflow
To install the nOps Agent click on the cluster's Configure to Optimize to begin data collection.
- API Key Setup : Generate a new API key for the nOps Agent Stack.
- Copy the custom command and run it in your command line.
- On Successful, Click Test Connectivity to confirm connectivity with the nOps Agent Stack.
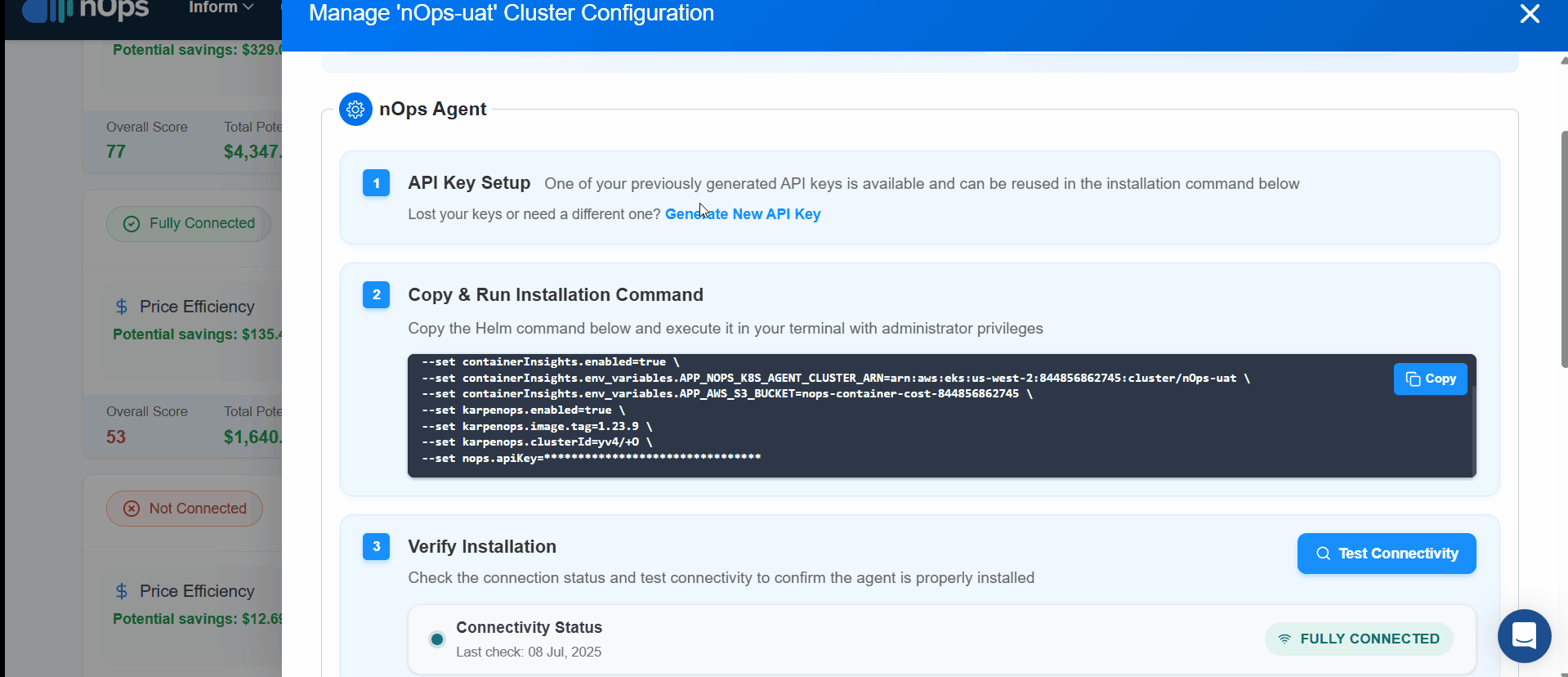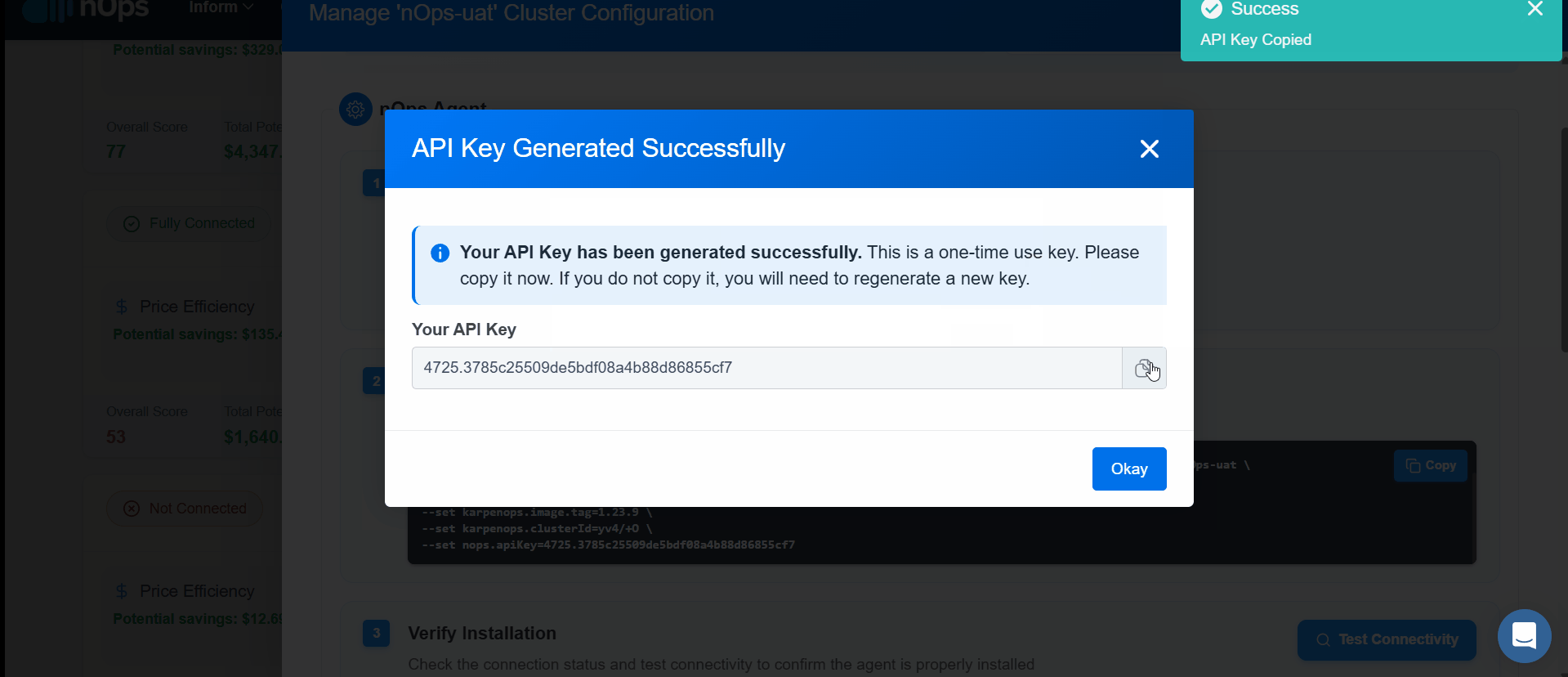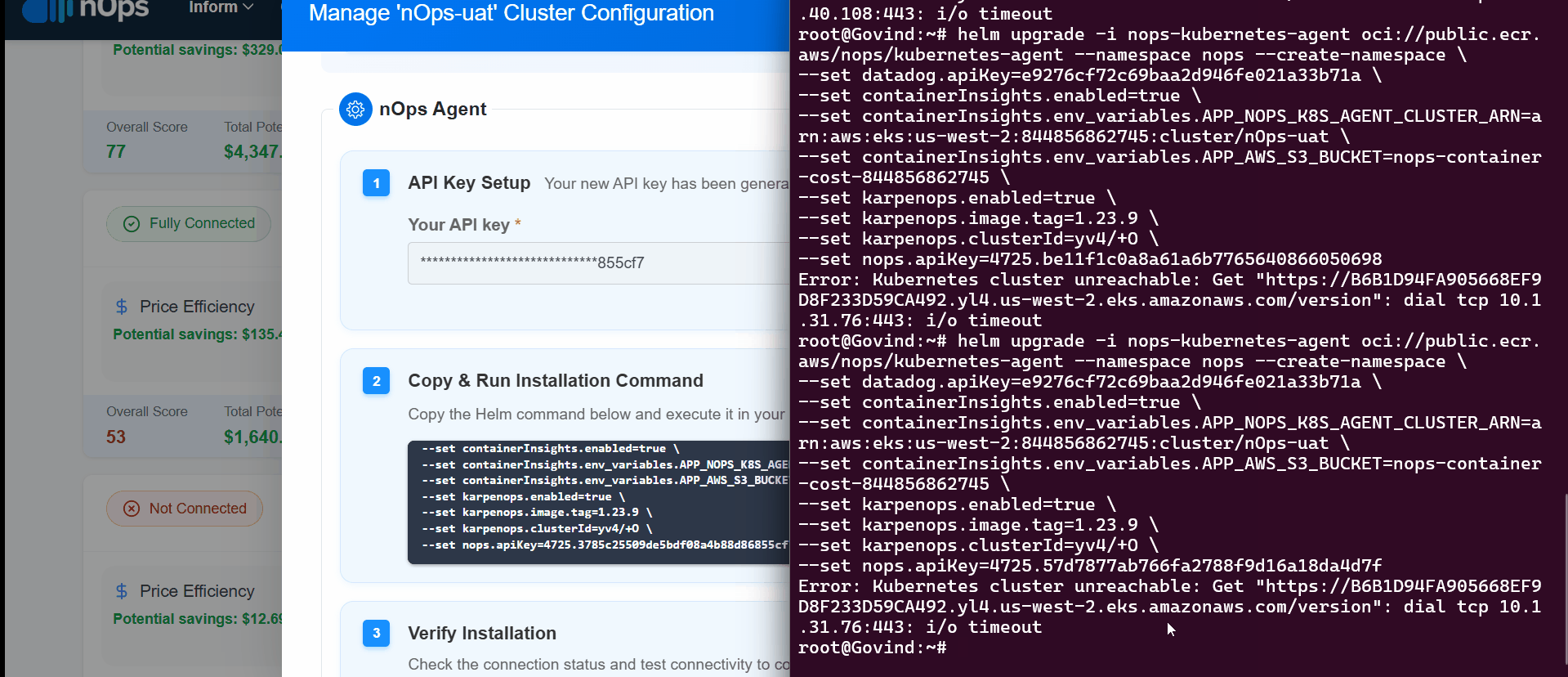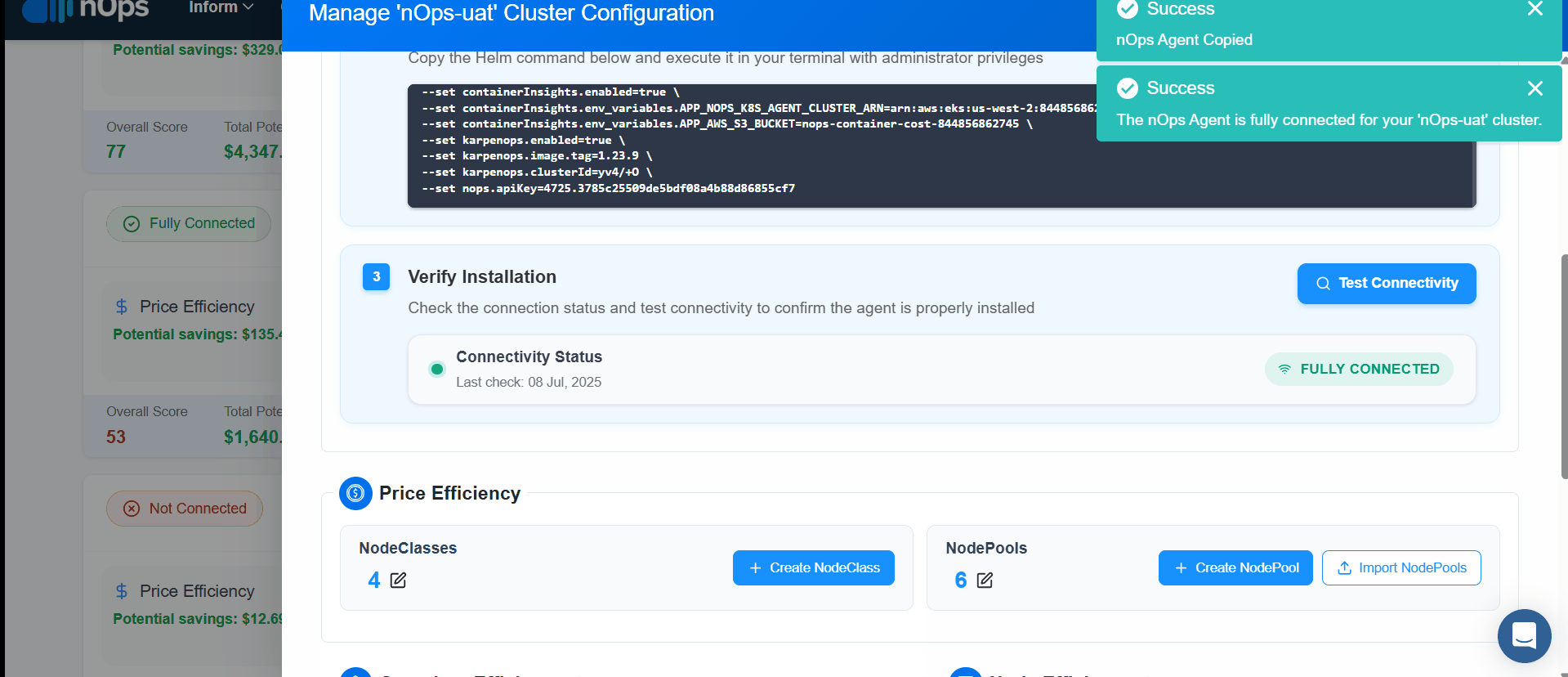
With this setup, your clusters are fully equipped to gather and upload data, providing comprehensive insights into your containerized workloads.
How the Container Insights Agent Works
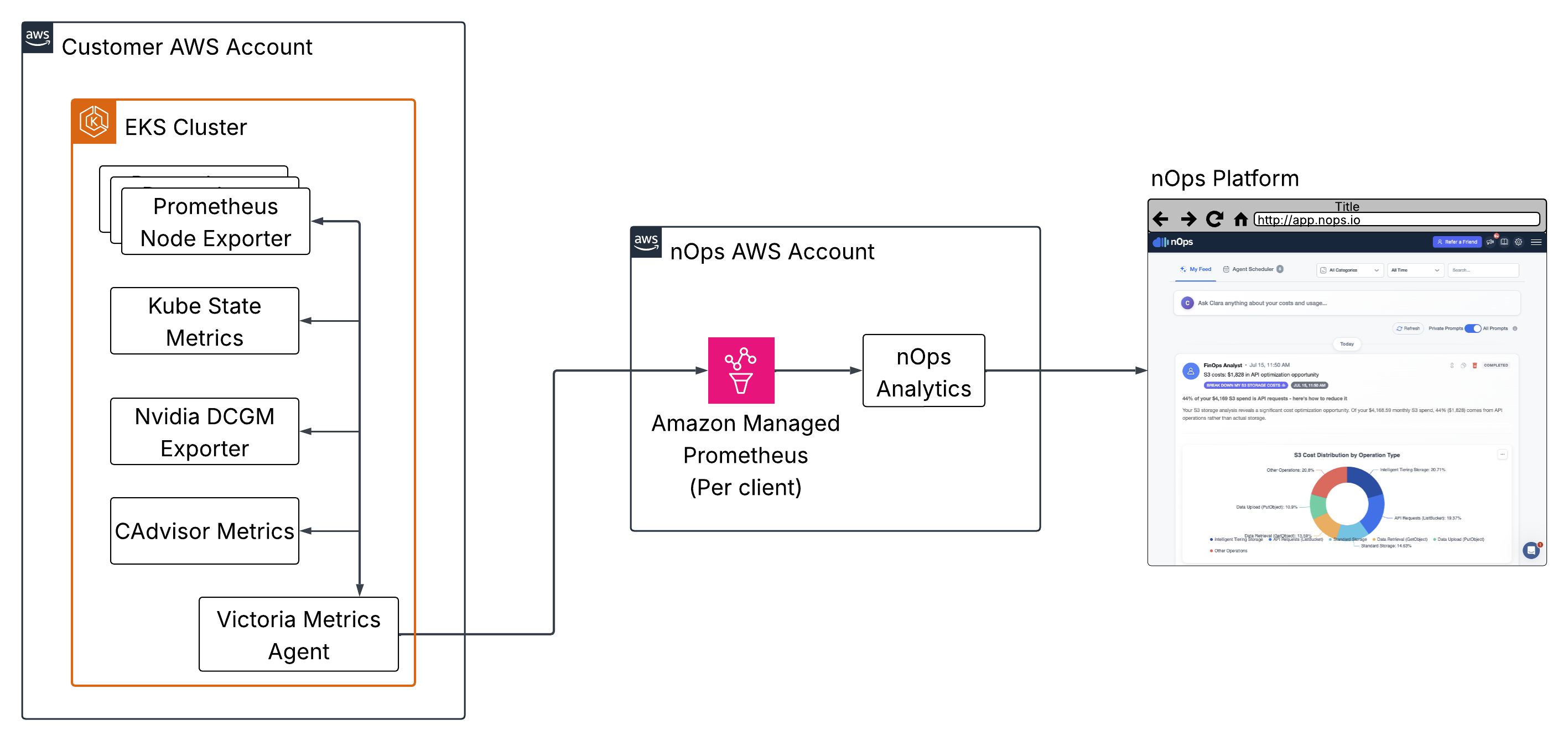
The agent operates through a series of off-the-shelf, open-source metrics exporters along with the VictoriaMetrics agent to forward metrics to Amazon Managed Prometheus.
-
Metrics Sources:
- Promethes Node Exporter: node level usage metrics
- Kube State Metrics: workload metrics from the Kubernetes API
- Nvidia DCGM Exporter: GPU metrics (if your nodes have GPUs)
- CAdvisor metrics: Container metrics from the
kubeletsalready in your cluster
-
VictoriaMetrics Agent: A ligtweight agent that scrapes the metrics sources outlined above and, using the Prometheus remote write protocol, forwards them to Amazon Managed Service for Prometheus
-
Amazon Managed Service for Prometheus: (AMP) A centralized metrics store managed by Amazon. Deployed in the nOps AWS environment. Data is partitioned by issuing one AMP workspace per customer.
-
nOps analytics: Data is queried from AMP and analyzed in nOps' AWS environment to drive all the features of the nOps Platform
How the nOps Vertical Pod Autoscaler Works
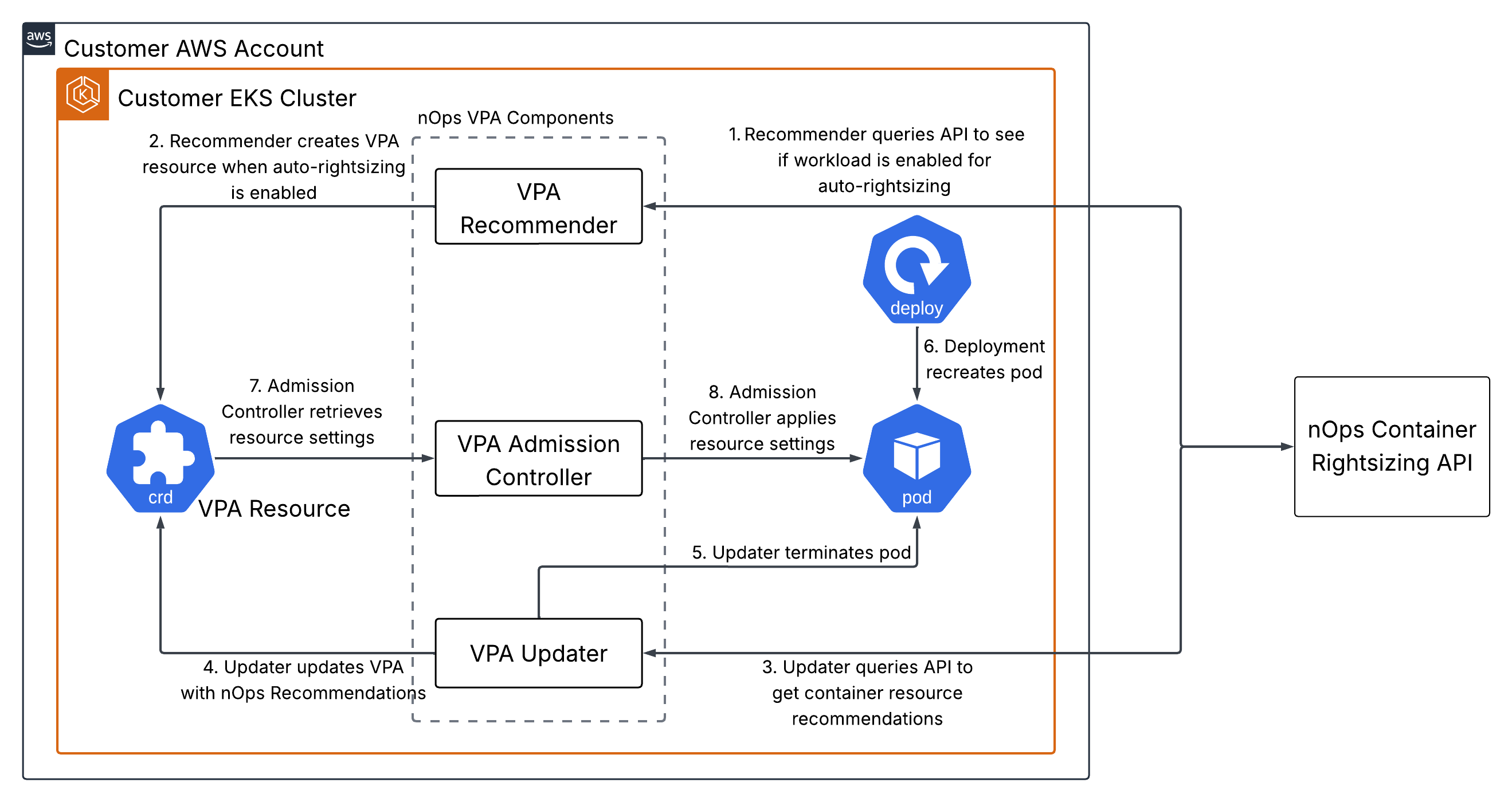
The nOps Vertical Pod Autoscaler is based on the open source vertical pod autoscaler component developed by Kubernetes. It uses a mutating webhook driven by an admission controller to apply resource recommendations to the workloads in your cluster. Recommended resource settings are tracked in VerticalPodAutoscaler (VPA) custom resources. The VPA custom resources used by the nOps VPA are namespaced to enable the nOps VPA to coexist with the upstream Kubernetes VPA in the same cluster.
How the Karpenops Agent Works
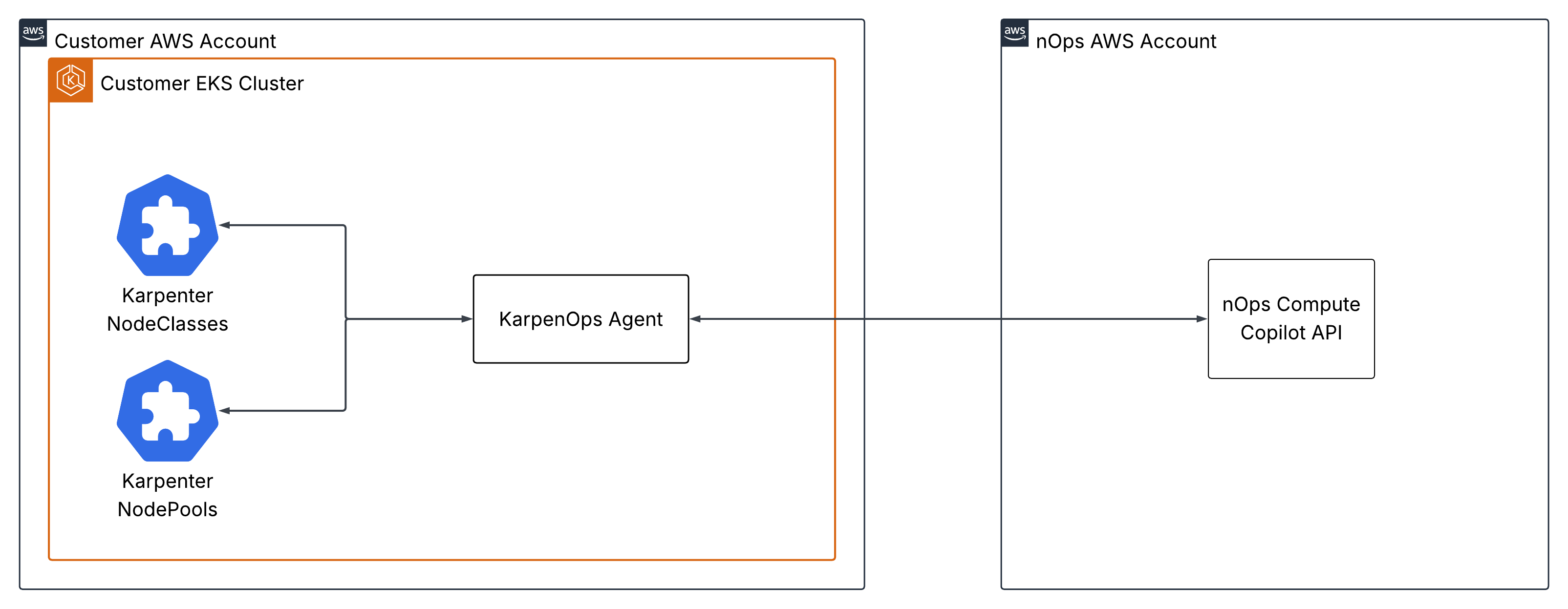
The Karpenops agent enables nOps Compute Copilot to optimize the Karpenter NodeClass and NodePool settings in your cluster. It is a simple agent that uses HTTPS polling to update the status of your NodePools and NodeClasses with the nOps API, and update your NodePools based on spot compute market scores and commitment utilization from the nOps API.
How the Data Fetcher Agent Works

The Data Fetcher Agent utilizes the Two-Way Messaging Pattern, leveraging Amazon SQS for real-time communication with nOps. This design ensures that Kubernetes data is promptly fetched and made available in your Cluster Dashboard for seamless, up-to-date visibility.
Encryption: The Data Fetcher Agent communicates securely with Amazon SQS using HTTPS, ensuring encryption in transit. At this time, Server-Side Encryption (SSE) for SQS queues is not enabled.
How the Image Tag Updater Works
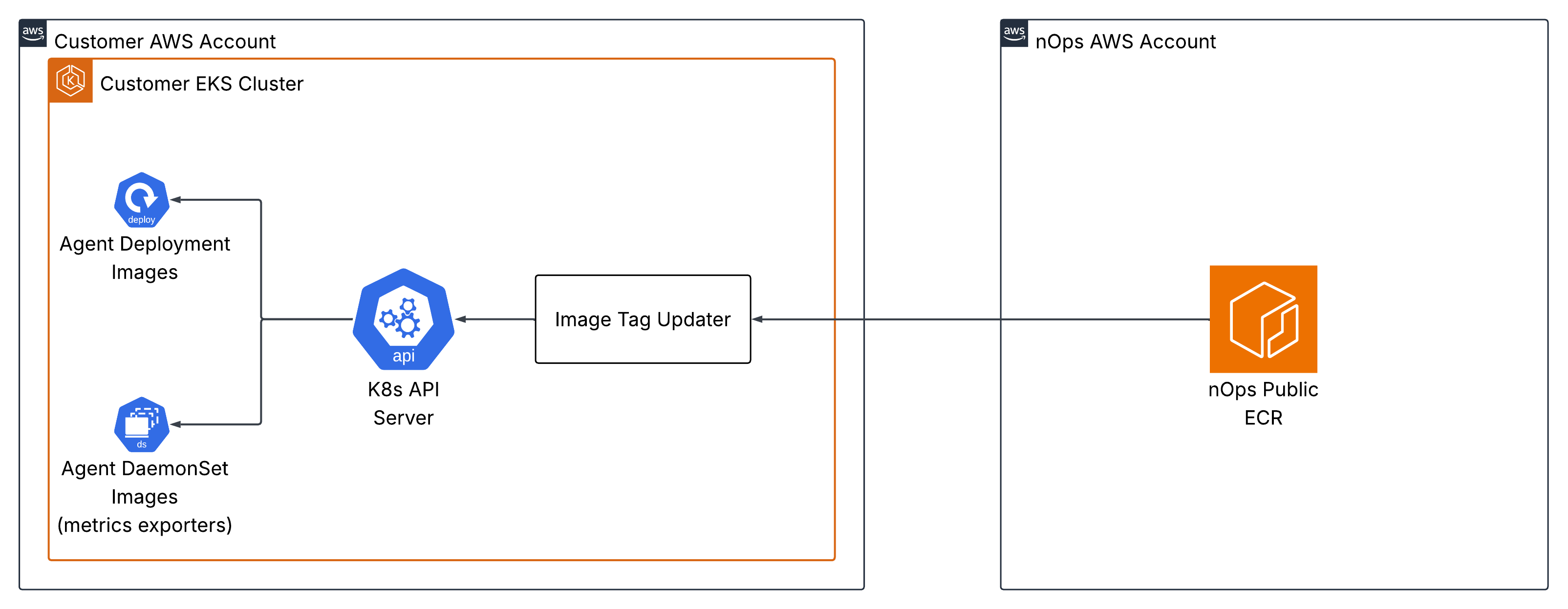
The image tag updater is a CronJob that is deployed and runs nightly at midnight. Upon execution, it scans the nOps public ECR repos for updated images, and if any are found, utilizes the Kubernetes API to update the deployments/daemonsets of the nOps Kubernetes Agent components with the new image tags.
Helm Configuration Reference
Recommended Installation Flow
Configuration starts in the nOps UI (Optimize → EKS Optimization). Selecting Configure to Optimize or Manage Configuration opens a modal that:
- Generates an nOps API key.
- Provides a Helm command targeting
oci://public.ecr.aws/nops/kubernetes-agentwith all required settings and credentials pre-populated.
Run that command as-is for standard installs. When cluster policies require adjustments, copy the Helm command and set additional configuration values on the command line using --set/--set-json or supply a values file via -f values.yaml.
Example helm command from the UI:
helm upgrade -i nops-kubernetes-agent oci://public.ecr.aws/nops/kubernetes-agent --namespace nops --create-namespace \
--set datadog.apiKey=********************** \
--set containerInsights.enabled=true \
--set containerInsights.centralized=true \
--set containerInsights.env_variables.APP_NOPS_K8S_AGENT_CLUSTER_ARN=arn:aws:eks:us-west-2:123456789012:cluster/my-sample-cluster \
--set containerInsights.ampID=********************* \
--set containerInsights.ampRegion=us-west-2 \
--set containerInsights.ampAccessKey=****************** \
--set containerInsights.ampSecretKey=************************* \
--set karpenops.enabled=true \
--set karpenops.image.tag=1.25.1 \
--set karpenops.clusterId=***** \
--set nops.apiKey=********************************
Required Values Provided by the UI
| Value path | Description | Where to find it |
|---|---|---|
nops.apiKey | Authenticates the agent stack with the nOps API. | Generated in the cluster configuration modal or Settings → API Key. |
containerInsights.env_variables.APP_NOPS_K8S_AGENT_CLUSTER_ARN | Identifies the EKS cluster in AMP and nOps backends. Unique per cluster. | Included in the cluster Helm command in the UI. |
containerInsights.ampID / containerInsights.ampRegion | Points the agent to your AMP workspace and region. Unique per nOps account. | Included in the cluster Helm command in the UI. |
containerInsights.ampAccessKey / containerInsights.ampSecretKey | Scoped AWS credentials for AMP remote-write. Unique per nOps account. | Included in the cluster Helm command in the UI. |
karpenops.clusterId | Internal identifier for Karpenter optimization. Unique per cluster | Included in the cluster Helm command in the UI for Karpenter clusters. |
datadog.apiKey | Optional key for support-assisted diagnostics. Unique per nOps account. | Included in the cluster Helm command in the UI. |
Global Scheduling & Metadata Controls
nops.global applies shared scheduling policies and metadata to most components (daemonsets such as the node exporter maintain their own rules).
| Value path | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
nops.global.nodeSelector | {} | Apply a node selector to all agent workloads (excluding Prometheus node-exporter and NVIDIA dcgm-exporter daemonsets). |
nops.global.tolerations | [] | Apply tolerations to all agent workloads to enable scheduling on tainted nodes. |
nops.global.affinity | {} | Apply affinities to all agent workloads (excluding Prometheus node-exporter and NVIDIA dcgm-exporter daemonsets). |
nops.global.labels | {} | Attach labels to every agent resource. Useful for ownership or cost-center metadata, etc. |
nops.global.annotations | {} | Attach annotations to all workloads (deployments, daemonsets, cronjobs), pods, and service resources. |
Example:
nops:
global:
# Node selectors limit where pods can run based on node labels.
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/os: linux
# Tolerations allow pods to run on nodes with specific taints.
tolerations:
- key: nops/agents
operator: Exists
effect: NoSchedule
# Labels are applied to all pods created by the chart.
labels:
cost-center: finops
# Affinity defines scheduling preferences for pods.
# In this example, pods will prefer (but not require) nodes
# labeled with "nops/role=compute".
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- weight: 100
preference:
matchExpressions:
- key: nops/role
operator: In
values:
- compute
annotations:
owner: platform
shared: global-default
Component-level settings (containerInsights.nodeSelector, etc.) remain available if a specific workload needs different scheduling or metadata.
When combining global and component-level scheduling or metadata, component keys win on collision. Keep shared keys consistent to avoid surprises.
Component-Specific Annotation fields
Set component fields instead of or alongside nops.global.annotations to add/override keys on a component-specific basis.
- Data Fetcher
- Workload:
dataFetcher.deploymentAnnotations - Pod:
dataFetcher.podAnnotations
- Workload:
- Karpenops
- Workload:
karpenops.deploymentAnnotations - Pod:
karpenops.podAnnotations - Service Account:
karpenops.serviceAccount.annotations
- Workload:
- Heartbeat Agent
- Workload:
heartbeat.deploymentAnnotations - Pod:
heartbeat.podAnnotations
- Workload:
- DCGM Exporter
- Workload:
dcgmExporter.daemonsetAnnotations - Pod:
dcgmExporter.podAnnotations - Service:
dcgmExporter.service.annotations
- Workload:
- Kube State Metrics
- Workload:
prometheus.kubeStateMetrics.annotations - Pod:
prometheus.kubeStateMetrics.podAnnotations - Service:
prometheus.kubeStateMetrics.service.annotations(merged withprometheus.io/scrapeif enabled)
- Workload:
- Prometheus Node Exporter
- Workload:
prometheus.nodeExporter.daemonsetAnnotations - Pod:
prometheus.nodeExporter.podAnnotations - Service:
prometheus.nodeExporter.service.annotations
- Workload:
- Victoria Metrics Agent (centralized/server mode)
- Workload:
victoriaMetrics.annotations - Pod:
victoriaMetrics.podAnnotations - Service Account:
victoriaMetrics.serviceAccount.annotations
- Workload:
- Image Tag Updater
- CronJob:
autoUpdater.cronjobAnnotations - Pod:
autoUpdater.podAnnotations
- CronJob:
Secrets & Credential Sources
| Value path | Usage | Guidance |
|---|---|---|
externalSecrets.enabled | Legacy integration with External Secrets Operator (secretStoreRef + data.apiKeys.remoteRef.key). | Still supported but superseded by customer-managed secrets. Prefer the operator-agnostic approach below. |
customerManagedSecrets.enabled | Reference Kubernetes secrets you provision in the nops namespace using any workflow (GitOps, SealedSecrets, manual kubectl). Populate apiSecretName, ampSecretName, etc. | Recommended when you manage secrets centrally; remove the matching --set flags from the Helm command. |
If both toggles stay false, the chart relies on credentials supplied directly through the UI-generated --set flags.
External Secrets Operator support
For details on configuring the external secrets operator, see the documentation page for external secrets operator support.
Customer Managed Secrets support
The customer managed secrets feature of the agent helm chart is an operator-agnostic facility for managing agent secrets externally.
It simply assumes that the secrets required by the agent will be present in a Kubernetes Secret (or possibly multiple Secrets) resource in the chart namespace (nops).
This Secret resource can be managed by any operator (External Secrets Operator/Vault/etc) or by hand if desired.
Example:
Assuming you have an operator managed secret called nops-secret, you can configure the agent Helm chart to use these secret by setting chart values as shown below.
Kubernetes secret, managed by your operator:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: nops-secret
namespace: nops
type: Opaque
data:
API_KEY: QUJDREVGR0hJSktMTU5PUA== # "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOP"
DD_KEY: ZGVtb19kYXRhZG9nX2tleQ== # "demo_datadog_key"
AMP_ACCESS_KEY: QU1QX0FDQ0VTU19LRVk= # "AMP_ACCESS_KEY"
AMP_SECRET_KEY: QU1QX1NFQ1JFVF9LRVkxMjM0NQ== # "AMP_SECRET_KEY12345"
Agent Helm chart values to set:
customerManagedSecrets:
enabled: true
apiSecretName: "nops-secret"
apiSecretKey: "API_KEY"
ddSecretName: "nops-secret"
ddSecretKey: "DD_KEY"
ampAccessName: "nops-secret"
ampAccessKey: "AMP_ACCESS_KEY"
ampSecretName: "nops-secret"
ampSecretKey: "AMP_SECRET_KEY"
Note that, at a minimum, you must provide a secret containing the API secret key, the AMP access key, and the AMP secret key. These do not need to be in the same Secret resource, but they must all be specified and managed by your operator, etc.
Disabling Components
We strive to make sure the default configuration of the agent helm chart provides valuable functionality with minimal configuration. However, if you determine that you need a custom configuration, some components of the agent helm chart can be disabled. If you have questions about disabling components, please consult nOps support.
| Feature | Toggle | Default | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Image Tag Updater | autoUpdater.enabled | true | Keeps images current; disable only if change control forbids automation. |
| Karpenops | karpenops.enabled | true in UI command | Disable on clusters without Karpenter or if you manage NodePools manually. |
| Container Rightsizing | containerRightsizing.enabled | true | Turn off to disabe nOps VPA (container rightsizing) automation |
| Datadog Agent | datadog.enabled | false | Enable temporarily when nOps support requests additional telemetry. |
| NVIDIA DCGM Exporter | dcgmExporter.enabled | true | Safe to leave enabled: pods will only be scheduled on nodes with GPUs; set false on GPU-free clusters. |
| Data Fetcher | dataFetcher.enabled | true | May be disabled for sensitive environments; dashboards relying on live workload data will lose detail. |
Example Helm commands
Only install Container Insights; disable all automation/integration components (container rightsizing, Karpenter, etc):
helm upgrade -i nops-kubernetes-agent oci://public.ecr.aws/nops/kubernetes-agent --namespace nops --create-namespace \
--set datadog.apiKey=********************** \
--set containerInsights.enabled=true \
--set containerInsights.centralized=true \
--set containerInsights.env_variables.APP_NOPS_K8S_AGENT_CLUSTER_ARN=arn:aws:eks:us-west-2:123456789012:cluster/my-sample-cluster \
--set containerInsights.ampID=********************* \
--set containerInsights.ampRegion=us-west-2 \
--set containerInsights.ampAccessKey=****************** \
--set containerInsights.ampSecretKey=************************* \
--set karpenops.enabled=false \
--set autoUpater.enabled=false \
--set dataFetcher.enabled=false \
--set containerRightsizing.enabled=false \
--set nops.apiKey=********************************
Only install Karpenter integration; disable all other components:
helm upgrade -i nops-kubernetes-agent oci://public.ecr.aws/nops/kubernetes-agent --namespace nops --create-namespace \
--set datadog.apiKey=******************************** \
--set containerInsights.env_variables.APP_NOPS_K8S_AGENT_CLUSTER_ARN=arn:aws:eks:us-west-2:123456789012:cluster/my-sample-cluster \
--set containerInsights.enabled=false \
--set autoUpater.enabled=false \
--set dataFetcher.enabled=false \
--set containerRightsizing.enabled=false \
--set karpenops.enabled=true \
--set karpenops.image.tag=1.25.1 \
--set karpenops.clusterId=***** \
--set nops.apiKey=********************************
(Note: The heartbeat agent is still installed in these configuration examples. Autoupdate functionality is not installed in these configuration examples.)
ArgoCD Reference
ArgoCD is a declarative, GitOps continuous delivery tool for Kubernetes. Using ArgoCD to manage the nOps Kubernetes Agent provides benefits such as version control, automated synchronization, and centralized configuration management across multiple clusters.
Recommended Installation Flow
Configuration starts in the nOps UI (Optimize → EKS Optimization). Selecting Configure to Optimize or Manage Configuration opens a modal that:
- Generates an nOps API key.
- Provides a Helm command with all required settings and credentials.
To use ArgoCD, extract the Helm values from the UI-generated command and convert them to ArgoCD Application parameters. For sensitive values, use ArgoCD's secret management features (see Secrets & Credential Sources below).
ArgoCD Application Structure
The nOps Kubernetes Agent Helm chart is deployed via an ArgoCD Application resource. The chart is hosted in AWS ECR as an OCI registry: oci://public.ecr.aws/nops/kubernetes-agent.
Key ArgoCD Application Fields
| Field | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
source.repoURL | OCI registry URL for the Helm chart | Always oci://public.ecr.aws/nops/kubernetes-agent |
source.chart | Helm chart name | Always kubernetes-agent |
source.targetRevision | Chart version to deploy | Use latest for automatic updates, or pin to a specific version (e.g., 1.0.0) |
source.helm.parameters | Helm values passed to the chart | Convert Helm --set flags to parameter objects |
destination.namespace | Target namespace for deployment | Defaults to nops |
syncPolicy.automated | Enable automatic synchronization | Recommended: prune: true, selfHeal: true |
Required Parameters
These parameters must be set in your ArgoCD Application. Obtain the values from the Helm command provided in the nOps UI:
| Parameter name | Description | Where to find it |
|---|---|---|
nops.apiKey | Authenticates the agent stack with the nOps API | Generated in the cluster configuration modal or Settings → API Key |
containerInsights.env_variables.APP_NOPS_K8S_AGENT_CLUSTER_ARN | Identifies the EKS cluster in AMP and nOps backends | Included in the cluster Helm command in the UI |
containerInsights.ampID | Points the agent to your AMP workspace | Included in the cluster Helm command in the UI |
containerInsights.ampRegion | AWS region for your AMP workspace | Included in the cluster Helm command in the UI |
containerInsights.ampAccessKey | AWS access key for AMP remote-write | Included in the cluster Helm command in the UI |
containerInsights.ampSecretKey | AWS secret key for AMP remote-write | Included in the cluster Helm command in the UI |
karpenops.clusterId | Internal identifier for Karpenter optimization | Included in the cluster Helm command in the UI for Karpenter clusters |
datadog.apiKey | Optional key for support-assisted diagnostics | Included in the cluster Helm command in the UI |
Example ArgoCD Application
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: nops-kubernetes-agent
namespace: argocd
finalizers:
- resources-finalizer.argocd.argoproj.io
labels:
name: nops-kubernetes-agent
spec:
project: default
source:
repoURL: oci://public.ecr.aws/nops/kubernetes-agent
chart: kubernetes-agent
targetRevision: latest
helm:
passCredentials: false
parameters:
- name: "datadog.apiKey"
value: "********************************"
- name: "containerInsights.enabled"
value: "true"
forceString: true
- name: "containerInsights.centralized"
value: "true"
forceString: true
- name: "containerInsights.env_variables.APP_NOPS_K8S_AGENT_CLUSTER_ARN"
value: "********************************"
- name: "containerInsights.ampID"
value: "********************************"
- name: "containerInsights.ampRegion"
value: "********************************"
- name: "containerInsights.ampAccessKey"
value: "********************************"
- name: "containerInsights.ampSecretKey"
value: "********************************"
- name: "nops.apiKey"
value: "********************************"
# Release name override
releaseName: nops-kubernetes-agent
skipCrds: false
# Destination cluster and namespace to deploy the application
destination:
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
namespace: nops
# Sync policy
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: true
allowEmpty: false
syncOptions:
- Validate=false
- CreateNamespace=true
- PrunePropagationPolicy=foreground
- PruneLast=true
retry:
limit: 5
backoff:
duration: 5s
factor: 2
maxDuration: 3m
revisionHistoryLimit: 3
Secrets & Credential Sources
ArgoCD provides several options for managing sensitive values in your Application configuration:
Option 1: Customer-Managed Secrets (Recommended)
Use Kubernetes Secrets managed by your GitOps workflow, External Secrets Operator, or other secret management tools. This approach keeps sensitive values out of your Git repository.
- Create Kubernetes Secrets in the
nopsnamespace containing the required credentials. - Enable
customerManagedSecretsin your ArgoCD Application parameters. - Reference the secret names and keys in the Helm values.
Example ArgoCD Application with Customer-Managed Secrets:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: nops-kubernetes-agent
namespace: argocd
spec:
source:
repoURL: oci://public.ecr.aws/nops/kubernetes-agent
chart: kubernetes-agent
targetRevision: latest
helm:
parameters:
- name: "customerManagedSecrets.enabled"
value: "true"
forceString: true
- name: "customerManagedSecrets.apiSecretName"
value: "nops-secret"
- name: "customerManagedSecrets.apiSecretKey"
value: "API_KEY"
- name: "customerManagedSecrets.ampAccessName"
value: "nops-secret"
- name: "customerManagedSecrets.ampAccessKey"
value: "AMP_ACCESS_KEY"
- name: "customerManagedSecrets.ampSecretName"
value: "nops-secret"
- name: "customerManagedSecrets.ampSecretKey"
value: "AMP_SECRET_KEY"
- name: "containerInsights.enabled"
value: "true"
forceString: true
- name: "containerInsights.centralized"
value: "true"
forceString: true
- name: "containerInsights.env_variables.APP_NOPS_K8S_AGENT_CLUSTER_ARN"
value: "arn:aws:eks:us-west-2:123456789012:cluster/my-sample-cluster"
destination:
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
namespace: nops
Option 2: ArgoCD Secrets
Store sensitive values in ArgoCD Secrets and reference them using valueFrom. This keeps secrets within ArgoCD's secret management system.
Example using ArgoCD Secret:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: nops-kubernetes-agent
namespace: argocd
spec:
source:
repoURL: oci://public.ecr.aws/nops/kubernetes-agent
chart: kubernetes-agent
targetRevision: latest
helm:
parameters:
- name: "nops.apiKey"
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: nops-credentials
key: apiKey
- name: "containerInsights.ampAccessKey"
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: nops-credentials
key: ampAccessKey
- name: "containerInsights.ampSecretKey"
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: nops-credentials
key: ampSecretKey
# ... other non-sensitive parameters
Option 3: External Secrets Operator Integration
If you're using External Secrets Operator, create ExternalSecret resources that sync secrets from your secret store (AWS Secrets Manager, HashiCorp Vault, etc.) to Kubernetes Secrets, then use Option 1 above.
Customizing Configuration
Adding Global Scheduling & Metadata
To apply global node selectors, tolerations, affinities, labels, or annotations, add parameters for nops.global.* values:
helm:
parameters:
- name: "nops.global.nodeSelector.kubernetes.io/os"
value: "linux"
- name: "nops.global.tolerations[0].key"
value: "nops/agents"
- name: "nops.global.tolerations[0].operator"
value: "Exists"
- name: "nops.global.tolerations[0].effect"
value: "NoSchedule"
- name: "nops.global.labels.cost-center"
value: "finops"
For complex nested values, consider using a values.yaml file in your Git repository and referencing it via source.helm.valueFiles.
Disabling Components
To disable specific components, set the corresponding *.enabled parameter to false:
helm:
parameters:
- name: "karpenops.enabled"
value: "false"
forceString: true
- name: "containerRightsizing.enabled"
value: "false"
forceString: true
- name: "dataFetcher.enabled"
value: "false"
forceString: true
Example Configurations
Container Insights Only (No Automation Components)
Deploy only the Container Insights agent, disabling all automation and integration components:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: nops-kubernetes-agent
namespace: argocd
spec:
source:
repoURL: oci://public.ecr.aws/nops/kubernetes-agent
chart: kubernetes-agent
targetRevision: latest
helm:
parameters:
- name: "containerInsights.enabled"
value: "true"
forceString: true
- name: "containerInsights.centralized"
value: "true"
forceString: true
- name: "containerInsights.env_variables.APP_NOPS_K8S_AGENT_CLUSTER_ARN"
value: "arn:aws:eks:us-west-2:123456789012:cluster/my-sample-cluster"
- name: "containerInsights.ampID"
value: "ws-*****************"
- name: "containerInsights.ampRegion"
value: "us-west-2"
- name: "karpenops.enabled"
value: "false"
forceString: true
- name: "autoUpdater.enabled"
value: "false"
forceString: true
- name: "dataFetcher.enabled"
value: "false"
forceString: true
- name: "containerRightsizing.enabled"
value: "false"
forceString: true
- name: "nops.apiKey"
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: nops-credentials
key: apiKey
- name: "containerInsights.ampAccessKey"
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: nops-credentials
key: ampAccessKey
- name: "containerInsights.ampSecretKey"
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: nops-credentials
key: ampSecretKey
destination:
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
namespace: nops
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: true
Karpenter Integration Only
Deploy only the Karpenter integration component:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: nops-kubernetes-agent
namespace: argocd
spec:
source:
repoURL: oci://public.ecr.aws/nops/kubernetes-agent
chart: kubernetes-agent
targetRevision: latest
helm:
parameters:
- name: "containerInsights.enabled"
value: "false"
forceString: true
- name: "autoUpdater.enabled"
value: "false"
forceString: true
- name: "dataFetcher.enabled"
value: "false"
forceString: true
- name: "containerRightsizing.enabled"
value: "false"
forceString: true
- name: "karpenops.enabled"
value: "true"
forceString: true
- name: "karpenops.image.tag"
value: "1.25.1"
- name: "karpenops.clusterId"
value: "*****"
- name: "nops.apiKey"
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: nops-credentials
key: apiKey
destination:
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
namespace: nops
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: true
Best Practices
-
Version Pinning: For production environments, pin
targetRevisionto a specific chart version instead of usinglatestto ensure reproducible deployments. -
Secret Management: Prefer customer-managed secrets or ArgoCD secrets over hardcoding sensitive values in Git repositories.
-
Sync Policies: Enable
automated.pruneandautomated.selfHealto keep your cluster state in sync with the desired configuration. -
Multi-Cluster Deployments: Use ArgoCD ApplicationSets or multiple Application resources to deploy the agent to multiple clusters with cluster-specific values.
-
Validation: Consider using ArgoCD's sync options like
Validate=true(if your cluster supports it) to validate Helm charts before deployment. -
Namespace Management: Ensure the
nopsnamespace exists before deploying, or usesyncOptions: [CreateNamespace=true]as shown in the example.
FAQ
-
Where can I get information about Security and Compliance?
You can find detailed reports on our stack and policies in this folder. -
Where can I find the CloudFormation template for inspection?
You can find the template here. -
Do containers run as root?
Most containers run as nobody with the exception of the datadog agent, which is non root but privileged, and the DCGM exporter which runs as root.
-
Which images are used in the deployment, and are they digitally signed?
Yes, the following images are used in our full deployment, and all of them have been digitally signed in our public ECR:- container-insights-agent
- k8s-heartbeat-agent
- k8s-data-fetcher-agent
- karpenops
- opencost
- alpine/k8s
- datadog agent
- kube-state-metrics
- nvidia/dcgm-exporter
- prometheus config-reloader
- prometheus node-exporter
- prometheus server
- victoriametric agent
These images are hosted in our public ECR to mitigate rate limit issues and are securely signed using AWS Signer. This ensures the integrity and authenticity of the images, supporting a reliable and trusted deployment pipeline.
-
What is the
nops-data-fetcheragent?The nOps Data Fetcher Agent provides real-time Kubernetes cluster insights, seamlessly integrating with your nOps dashboard. With this agent, you can visualize live data from your cluster directly within the Workloads tab, conveniently located next to the Nodes tab. To facilitate communication with nOps, the agent leverages an Amazon SQS queue for efficient and reliable data transfer.
-
Where do I supply cluster-specific IDs and AMP credentials?
Use the Helm command shown in the configuration modal. It already sets the nOps API key, AMP workspace ID and keys, and the cluster ARN. If you move to customer-managed secrets, create those secrets first, then remove the corresponding--setflags from the command. -
Can I disable Karpenops or other optional components?
Yes—set the relevant*.enabledvalue (for examplekarpenops.enabled: false) in your override file. Keep Container Insights, VictoriaMetrics, Data Fetcher, and Heartbeat enabled so the nOps platform continues to receive metrics and health signals. -
How do I add tolerations for tainted system nodes?
Add them undernops.global.tolerations(preferred) or within the specific component’stolerationslist. The chart merges global and component-level tolerations, so you only need to define each entry once.