Getting Started with Compute Copilot’s EKS Page: Metrics & Management
Get insights and metrics for all your EKS clusters on the EKS Clusters page in Compute Copilot to understand your cluster efficiency. The Compute Copilot’s EKS page provides quick access to key metrics for all your EKS clusters. From this page, you can navigate to individual clusters to configure them on nOps for Compute Copilot and Business Context+ (BC+), view container utilization metrics, and access rightsizing recommendations. This documentation will guide you through how to use the EKS page.
What is Compute Copilot?
Compute Copilot is a powerful service designed to automatically optimize compute-based workloads, reducing costs on AWS EKS by intelligently migrating EC2 instances to Spot instances using machine learning algorithms.
Learn more about how Compute Copilot for EKS can help you to put your EKS cost optimization on auto-pilot here.
What is Business Context+ (BC+)?
BC+ helps you understand and allocate 100% of your AWS costs, from your largest resources down to individual container costs. Click here to learn more about BC+.”%
How to Access the EKS Page for Compute Copilot?
To access the EKS page, navigate to Compute Copilot → EKS from the nOps dashboard.
You can also see how to access the page in the screen recording below:
Metrics Available in the EKS Page
As shown in the screen recording above, the EKS page features various cards and charts displaying key information about your EKS clusters. This page aggregates metrics across all your clusters that are correctly configured.
Here’s an explanation of each card:
Cost Breakdown
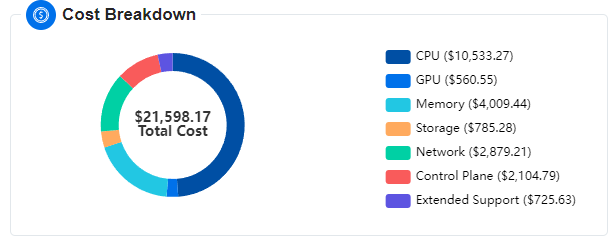
The Cost Breakdown chart on the EKS page provides a clear view of how costs are distributed across different components of your EKS clusters. This pie chart categorizes costs into several key areas, helping you understand where your budget is allocated. Here’s what each category represents:
-
CPU: This section shows the costs associated with the compute instances used by your clusters. It includes expenses related to the number of virtual CPUs and the types of instances in use.
-
GPU: This part highlights the costs for GPU resources utilized by your clusters. If your workloads use GPU instances, their associated costs are reflected here.
-
Memory: This category covers the expenses related to the amount of RAM allocated to your clusters. It includes costs based on memory usage.
-
Storage: This section represents the costs for various storage services, such as volumes and snapshots. It includes charges for storing and managing data within your clusters.
-
Network: This part accounts for costs associated with data transfer, NAT gateways, and load balancers. It includes charges for network-related services and data movement.
-
Extended Support: This category reflects additional charges incurred when your EKS clusters are not updated to the latest version. AWS applies these charges as a penalty for running outdated versions, which can include costs for extended support services.
-
Control Plane: This section includes costs not classified under the above categories. It covers miscellaneous expenses related to the management and operation of your clusters.
Number of Clusters
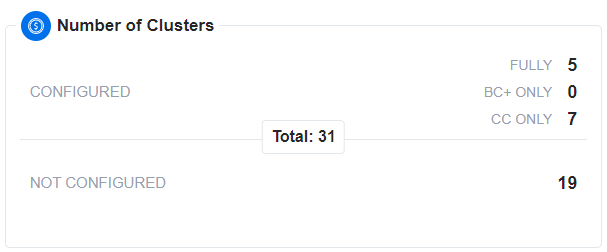
The Number of Clusters card on the EKS page provides an overview of your clusters and their configuration status. This card helps you quickly assess how many clusters you have and their current setup. Here’s a breakdown of what each status means:
- Configured:
- Fully: Displays the number of clusters where all necessary nOps agents and configurations are installed. For example, “Fully 5” indicates that 5 clusters have complete setup with all required agents and configurations on nOps Compute Copilot.
- BC+ Only: Shows the number of clusters that have only the BC+ agent installed. For instance, “BC+ only 3” means that 3 clusters have the BC+ agent but do not have the Compute Copilot agent installed.
- CC Only: Represents clusters where Compute Copilot is configured, regardless of whether they use the Compute Copilot agent or not. For example, “CC Only 4” means that 4 clusters have Compute Copilot configured. Note that an agent is required only for clusters using Karpenter, not for those using Cluster Autoscaler.
- Not Configured: Represents clusters that have no configuration or agents installed. These clusters are not yet set up for monitoring or management.
Container Utilization
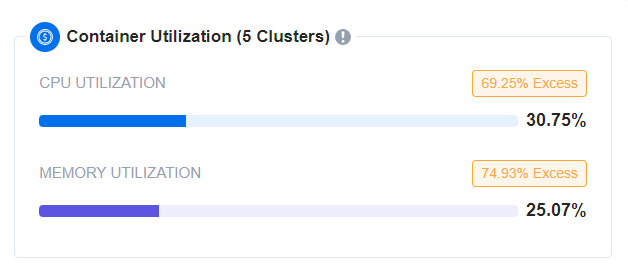
The Container Utilization card on the EKS page provides an overview of how efficiently your cluster’s CPU and memory resources are being used. This card helps you monitor both utilization and excess for these resources, giving you insights into potential areas for optimization. Here’s how it works:
-
CPU Utilization: A line graph indicating CPU utilization percentage and excess. The length of the blue line corresponds to the utilization percentage. Hovering over the line reveals detailed information, including requested CPU, used CPU, and excess CPU.
-
Memory Utilization: A similar line graph for memory, showing the utilization percentage and excess. The blue line’s length represents the memory utilization percentage. Hovering over the line shows requested memory, used memory, and excess memory.
Compute Copilot Opportunities
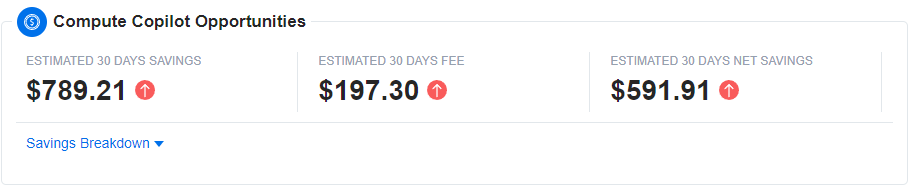
The Compute Copilot Opportunities card provides insights into potential cost savings and fees associated with using Compute Copilot. This card includes the following fields:
-
Estimated 30 Days Savings: Shows the projected savings you could achieve over the next 30 days by using Compute Copilot. This estimate helps you understand the financial benefits of optimizing your clusters with Compute Copilot.
-
Estimated 30 Days Fee: Displays the estimated fees associated with using Compute Copilot over the next 30 days. This includes any charges related to the service, giving you a clear picture of the costs involved.
-
Estimated 30 Days Net Savings: Calculates the net savings by subtracting the estimated fees from the estimated savings. This figure represents the overall financial benefit you can expect after accounting for the costs of using Compute Copilot.
Compute Copilot Realizations
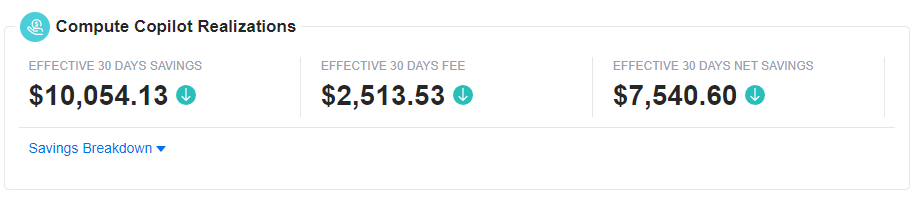
The Compute Copilot Realizations card offers a summary of the actual financial impacts achieved through the use of Compute Copilot. It includes the following fields:
-
Effective 30 Days Savings: Displays the actual savings realized over the past 30 days as a result of using Compute Copilot. This figure reflects the real financial benefits observed, providing insight into how well Compute Copilot has performed in reducing costs.
-
Effective 30 Days Fee: Shows the actual fees incurred over the past 30 days for using Compute Copilot. This includes any service-related charges that have been billed, giving you a clear understanding of the costs associated with the service.
-
Effective 30 Days Net Savings: Calculates the net savings by subtracting the effective fees from the effective savings. This net figure represents the actual financial benefit after accounting for the costs of using Compute Copilot, allowing you to see the true impact on your budget.
Cost Over Time
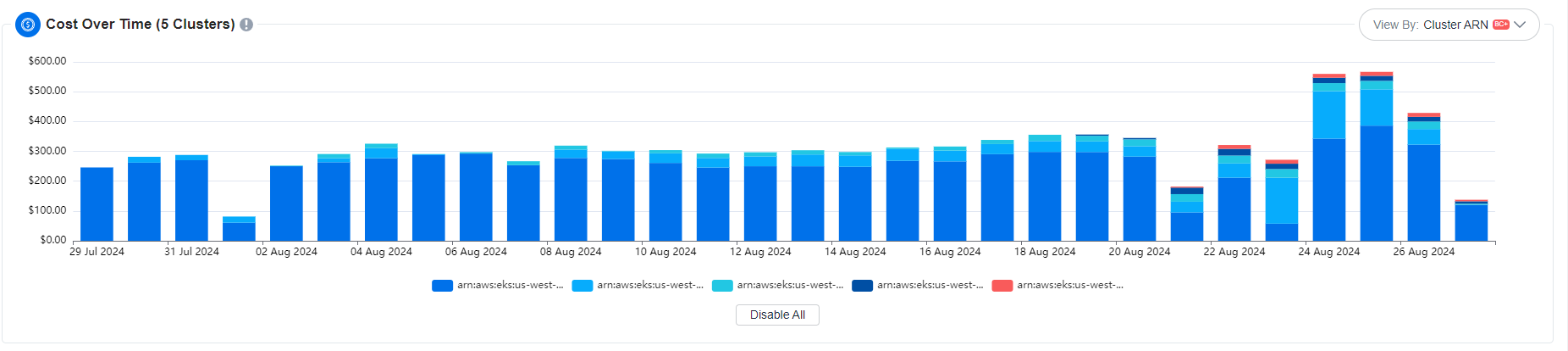
The Cost Over Time chart visualizes the cost trends for your EKS clusters with the BC+ agent installed. It provides a historical view of your cluster costs, allowing you to track how expenses change over time. This chart helps you identify cost patterns and make informed decisions to optimize your spending.
Cluster List Table
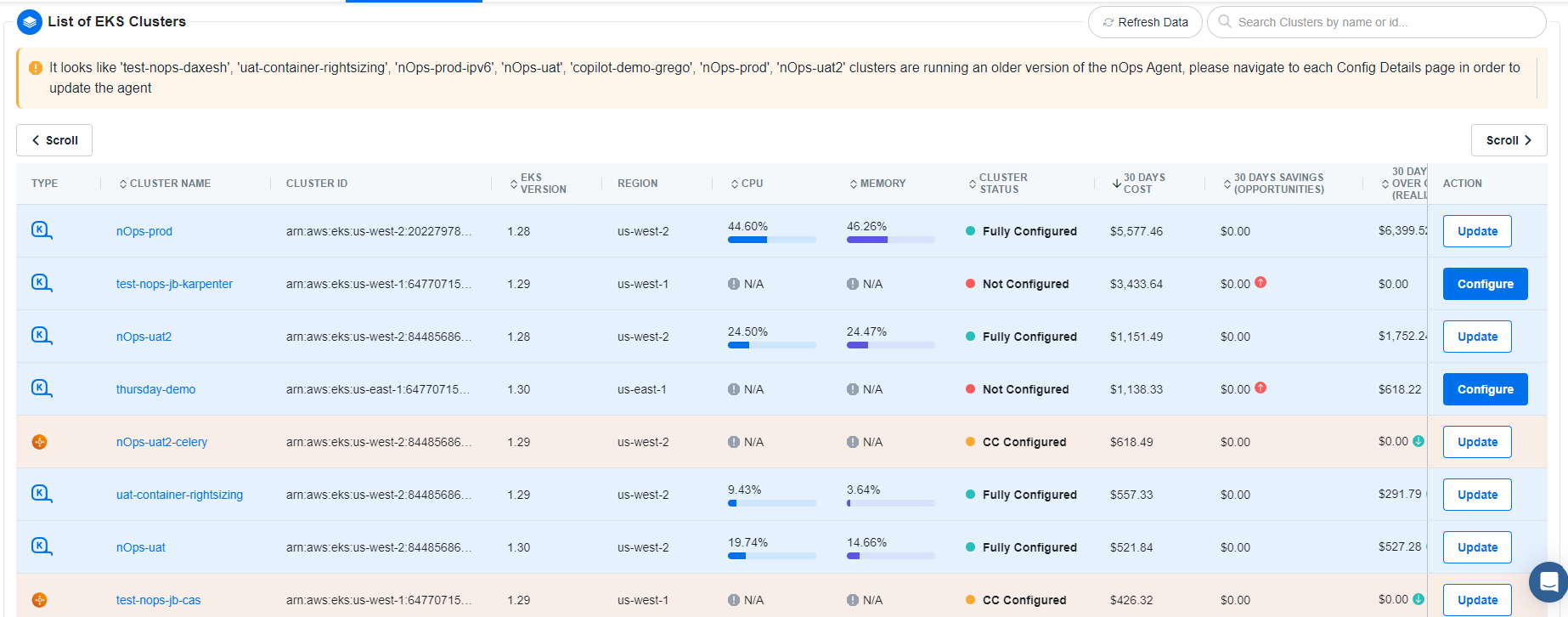
The Cluster List Table provides a comprehensive overview of your EKS clusters, displaying key information and metrics to help you manage and monitor your clusters efficiently. The table includes the following columns:
-
Type: Indicates the type of cluster, such as Cluster Autoscaler, Karpenter, or Undetermined.
-
Cluster Name: The name assigned to each cluster. Clicking on the cluster name will open the cluster’s dashboard for detailed insights.
-
ID: The Amazon Resource Name (ARN) for the cluster, providing a unique identifier.
-
EKS Version: Shows the version of Amazon EKS running on the cluster.
-
Region: Displays the AWS region where the cluster is located.
-
CPU: Represents the CPU utilization percentage for the cluster, shown as a blue line indicating the percentage. This metric is available only for clusters with the BC+ agent installed.
-
Memory: Displays the memory utilization percentage, similarly shown with a blue line. Like CPU metrics, this is available only for clusters with the BC+ agent.
-
Cluster Status: Provides the configuration status of each cluster, which can be Fully Configured, Not Configured, CC Configured, or BC+ Configured.
-
30 Days Cost: Shows the total cost incurred by the cluster over the past 30 days.
-
30 Days Savings Opportunities: Indicates the potential savings opportunities identified by Compute Copilot for the cluster over the past 30 days.
-
30 Days Savings Over On-Demand: Displays the savings achieved by using Compute Copilot compared to on-demand pricing for the past 30 days.
-
Action: Contains a button that opens a modal for configuring the cluster. This allows users to view and modify the cluster’s settings.
How to Configure Your Cluster
To set up your EKS clusters, follow the guides below based on your preferred tool:
- Configure Compute Copilot for Karpenter: Instructions for setting up Compute Copilot with Karpenter.
- Configure Compute Copilot for Cluster Autoscaler: Instructions for setting up Compute Copilot with Cluster Autoscaler.
Ensure you have Karpenter or Cluster Autoscaler configured as prerequisites before following these guides.
Back to top Home